Ik heb ooit een blog gevonden met daarin een goed verhaal omtrent wachtwoorden. De link van de blog heb ik niet meer, het verhaal nog wel:
With all of our advances in security technology, one aspect remains constant: passwords still play a central role in system security. The difficulty with passwords is that all too often they are the easiest security mechanism to defeat. Although we can use technology and policy to make passwords stronger, we are still fighting the weakest point in any system: the human element.
Ultimately the goal is to get users to choose better passwords. However, it is not always clear how to achieve that goal. The problem is that as creative as humans are, we are way too predictable. If I asked you to make a list of totally random words, inevitably some sort of pattern will emerge in your list. Selecting good passwords requires education. System administrators need to be educated and that education needs to be passed on to end users. This article is meant to bring you closer to understanding passwords in Windows 2000 and XP by addressing common password myths.
Tags
Howto
(51)
Free Software
(35)
Powershell
(33)
Windows Server
(23)
AD
(16)
Hyper-V
(16)
Exchange
(13)
Office
(13)
Group Policy
(10)
Windows Server 2012
(9)
Scripts
(7)
Symantec BE
(5)
Windows 8
(5)
Cisco
(4)
TMG
(4)
Terminal Server
(4)
Cluster
(3)
HP
(3)
RDS
(3)
UAG
(3)
Citrix
(2)
DC
(2)
DNS
(2)
IE10
(2)
OpenID
(2)
PKI
(2)
SCVMM
(2)
Windows Live
(2)
iLO
(2)
Backup
(1)
DPM
(1)
Fileserver
(1)
IE
(1)
SQL; DPM
(1)
Security
(1)
Sharepoint
(1)
Switch
(1)
VMWare
(1)
Veeam
(1)
maandag 3 oktober 2011
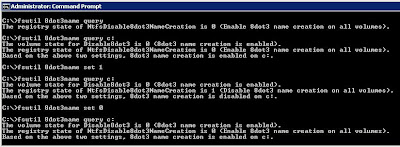
Disable8dot3 on Terminal Server Farm
Hieronder een verhaal waarom je 8dot3 moet uitzetten op een Terminal Server Farm (indien mogelijk).
Currenty i’m on the way to deploy a Windows Server 2008 R2 terminal server farm.
One server is already up and running productive and the other is one step before going online. I work a lot of with GPO’s and user roaming profiles, to ensure to have exactly the same configuration on the new server for all users. Also i use control panel restrictions to display only neccessary .CPL’s to the user.
And one special control panel addin, what is shipped with the MS Office suite ML32CFG.CPL (responsilbe for configuring MS Outlook MAPI Profile), i discovered how important it is, to ensure that applications have to be installed in the same order as on the other terminal servers.
Why, you may ask….because, of the 8dot3-names (8.3) and the windows internal file/path handling. In some cases the OS calls an an application it tries to use the 8dot3 path / name.
The control panel addin on the new server was registered successfully during the installation, and i could open it. But if i tried to open the CPL with my test user, what is already using the saved roaming profile, the addin would not open. Also the icon in the control panel window was different against to the other server.
So what happend? With Sysinternals Process Moinitor (PROCMON.EXE) I did a little bit research on both servers, and found out that the 8dot3 name of the MS Office path between both servers is different because i didn’t keep in mind the order, how i installed the applications on the new TS.
Server 1: (C:PROGRA~2\MICROS~1\Office12\MLCFG32.CPL)
Server 2: (C:PROGRA~2\MICROS~2\Office12\MLCFG32.CPL)
To solve the problem, i had no chance uninstall the application what occupies the 8dot3 name, uninstall office and reinstall office and the other application again. After reinstalling MS Office suite, the right 8dot3 name was assigned tho the new installation.
Zie voor extra info ook mijn blog over NTFS Hacks:
http://salfischberger.blogspot.com/2011/10/diverse-tips-hacks-betreft-filesystem.html
Currenty i’m on the way to deploy a Windows Server 2008 R2 terminal server farm.
One server is already up and running productive and the other is one step before going online. I work a lot of with GPO’s and user roaming profiles, to ensure to have exactly the same configuration on the new server for all users. Also i use control panel restrictions to display only neccessary .CPL’s to the user.
And one special control panel addin, what is shipped with the MS Office suite ML32CFG.CPL (responsilbe for configuring MS Outlook MAPI Profile), i discovered how important it is, to ensure that applications have to be installed in the same order as on the other terminal servers.
Why, you may ask….because, of the 8dot3-names (8.3) and the windows internal file/path handling. In some cases the OS calls an an application it tries to use the 8dot3 path / name.
The control panel addin on the new server was registered successfully during the installation, and i could open it. But if i tried to open the CPL with my test user, what is already using the saved roaming profile, the addin would not open. Also the icon in the control panel window was different against to the other server.
So what happend? With Sysinternals Process Moinitor (PROCMON.EXE) I did a little bit research on both servers, and found out that the 8dot3 name of the MS Office path between both servers is different because i didn’t keep in mind the order, how i installed the applications on the new TS.
Server 1: (C:PROGRA~2\MICROS~1\Office12\MLCFG32.CPL)
Server 2: (C:PROGRA~2\MICROS~2\Office12\MLCFG32.CPL)
To solve the problem, i had no chance uninstall the application what occupies the 8dot3 name, uninstall office and reinstall office and the other application again. After reinstalling MS Office suite, the right 8dot3 name was assigned tho the new installation.
Zie voor extra info ook mijn blog over NTFS Hacks:
http://salfischberger.blogspot.com/2011/10/diverse-tips-hacks-betreft-filesystem.html
Windows Server Performance Team: Performance Tuning Guidelines for Windows Server 2008 R2
http://blogs.technet.com/b/winserverperformance/archive/2009/07/14/performance-tuning-guidelines-for-windows-server-2008-r2-released.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/hardware/gg463392
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/hardware/gg463392
Windows Server Performance Team: Increase VMBus buffer sizes to increase network throughput to guest VMs
The Windows Server Performance team have done a really interesting post on how to optimize network performance inside of virtual machines by increasing the size of the VMBus buffers used by our network adapters. They also do a very good job of explaining the causes and implications of performance issues around virtual networking – so go check it out:
http://blogs.technet.com/winserverperformance/archive/2010/02/02/increase-vmbus-buffer-sizes-to-increase-network-throughput-to-guest-vms.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/winserverperformance/archive/2010/02/02/increase-vmbus-buffer-sizes-to-increase-network-throughput-to-guest-vms.aspx
NIC Teaming met Hyper-V
Wil je in Hyper-V gebruik maken van NIC Teaming dan moet zal er gebruik moeten gemaakt worden van de teaming software van HP (of andere OEMs).
(Microsoft is leaving NIC teaming to the OEM’s such as HP, Broadcom, Dell and IBM.This means that getting virtual network redundancy will rely on a Hyper-V friendly version of the HP Network Configuration Utility.)
BELANGRIJK:
Order of installation
To use HP ProLiant Network Teaming Software with Windows Server 2008 with Hyper-V, the software must be installed and enabled in the following order:
1. Install and enable the latest version of Hyper-V from Microsoft.
2. Install and enable the HP ProLiant Network Teaming Software.
NOTE
If the teaming software is installed first, the network adapters may cease passing traffic. The resolution to this issue is to uninstall both the HP teaming software and Hyper-V, reboot the server and then reinstall Hyper-V and the teaming software.
Bron: http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01663264/c01663264.pdf
(Microsoft is leaving NIC teaming to the OEM’s such as HP, Broadcom, Dell and IBM.This means that getting virtual network redundancy will rely on a Hyper-V friendly version of the HP Network Configuration Utility.)
BELANGRIJK:
Order of installation
To use HP ProLiant Network Teaming Software with Windows Server 2008 with Hyper-V, the software must be installed and enabled in the following order:
1. Install and enable the latest version of Hyper-V from Microsoft.
2. Install and enable the HP ProLiant Network Teaming Software.
NOTE
If the teaming software is installed first, the network adapters may cease passing traffic. The resolution to this issue is to uninstall both the HP teaming software and Hyper-V, reboot the server and then reinstall Hyper-V and the teaming software.
Bron: http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01663264/c01663264.pdf
Installatie Hyper-V op HP ML350G5
Hieronder de stappen:
- Download de laatste firmware CD van de HP site en gebruik deze om de hardware in de server van de laatste firmware versie te voorzien.
- Installeer Windows Server 2008 R2 (Standard)
- Wijzig eventueel de Computernaam en IP-adressen
- Installeer Powershell
- Werk Windows bij met de laatste updates
- Voor het uitvoeren van de setup van de Proliant Support Package (PSP) dient de SNMP service geinstalleerd te worden (serverManagerCMD -i snmp-services), anders kan de HP Insight Management Agent niet geinstalleerd worden.
- Installeer de laatste HP Proliant Support Package voor Windows Server 2008 R2 via HP Drivers ML350G5 maar installeer geen NIC Teaming Software (zie http://salfischberger.blogspot.com/2011/10/nic-teaming-met-hyper-v.html)
- Tijdens de installatie van PSP kan de HP Insight Management Agent geconfigureerd worden: Voeg iig de Administrators groep toe aan de Administrators en bij User Acces kies je voor Local Access – Administrator (grant full…..) en bij Trust Mode – Trust All. Vervolgens zet je de SNMP datacollection interval op 10 minuten en enable je de service.
- De “HP Network Configuration Utility” mag je nog niet installeren (deselect). Installeer deze pas nadat je Hyper-V hebt geinstalleerd. http://h20000.www2.hp.com/bc/docs/support/SupportManual/c01663264/c01663264.pdf.
- Bij de eigenschappen van de SNMP service voeg je op het tabblad security nog Community Rights “READ ONLY” aan de Community Groep “{mysecPublic148}” en “READ WRITE” aan de Community groep “{mysecPrivate149}” toe. Dit om bij de HP System Management Homepage wat meer informatie te kunnen zien.
- PSP installeer je alleen op de host server niet op de guest servers
- Via de RBSU (BIOS) zet je de “No-Execute Memory Protection” en de “Intel(R) Virtualization Technology” op enabled.
- Nu activeer je de role “Hyper-V”
Backing up Virtual Machines using Windows Server Backup in Server 2008 R2
Hieronder een blogpost van hoe je VMs in Windows 2008R2 kunt backuppen mbv Windows Server Backup.
Even een puntje van aandacht: Indien je VMs hiermee wilt backuppen dan kan dat alleen maar door het hele volume te backuppen. Je kunt niet alleen de vhd file backuppen.
Ook als je een VM wilt restoren, kan dat alleen maar door het hele volume te restoren.
Persoonlijk nog niet getest maar dat ga ik zeker doen.
http://mindre.net/post/Backing-up-Virtual-Machines-using-Windows-Server-Backup-in-Server-2008-R2.aspx
of:
http://www.virtualizationadmin.com/articles-tutorials/microsoft-hyper-v-articles/backup-recovery/installing-configuring-windows-server-backup-hyper-v.html
of bekijk onderstaande video:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windowsserver/dd775213.aspx
RECOVERY:
Om een individuele VM te restoren moet je de volgende commando’s uitvoeren:
In CMD:
Voer het commando: “wbadmin get versions” uit om te kijken welke backups aanwezig zijn.
Voer vervolgens het commando: “wbadmin get items -version:10/09/2010-10:08″ uit om de items in de backup te bekijken.
Onder het kopje “Application = Hyper-V” zie je GUIDs van de verschillende VMs.
Om te zien welke GUID bij welke VM hoort moet je onderstaand Powershell commando uitvoeren:
get-wmiobject -namespace “root\virtualization” -query “select * from msvm_computersystem” | format-table -property name, elementname
Als je onderstaand Powershell script in een ps1 opslaat en scheduled dan krijg je voortaan ook meldingen per email ofdat je backup gelukt is of niet.
===============================
$maxHours = 24
$email = “your@mail.net”
$smtpServer = “stmp.mail.net”
$sendSuccess = $true
## Script ————————————————————
Add-Pssnapin Windows.serverbackup
$summary = Get-WBSummary
$timeBetween = [DateTime]::Now – $summary.LastSuccessfulBackupTime
$computerName = get-content env:computername
if ($summary -eq $null)
{
$smtp = new-object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($email, $email, “BackupCheck.ps1 failed on $computerName”, “BackupCheck.ps1 failed with unknown error.”)
}
elseif ($timeBetween.TotalHours -gt $maxHours)
{
$smtp = new-object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($email, $email, “Windows Server Backup on $computerName failed”, “Last successfull backup on $computerName was at ” + $summary.LastSuccessfulBackupTime)
}
elseif ($sendSuccess)
{
$smtp = new-object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($email, $email, “Windows Server Backup on $computerName was successfull”, “Last backup on $computerName was successfull at ” + $summary.LastSuccessfulBackupTime)
}
==============================
Mbv de Windows Recovery Environment zou het mogelijk moeten zijn om de gehele server inclusief de VM terug te zetten.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766048(WS.10).aspx
Even een puntje van aandacht: Indien je VMs hiermee wilt backuppen dan kan dat alleen maar door het hele volume te backuppen. Je kunt niet alleen de vhd file backuppen.
Ook als je een VM wilt restoren, kan dat alleen maar door het hele volume te restoren.
Persoonlijk nog niet getest maar dat ga ik zeker doen.
http://mindre.net/post/Backing-up-Virtual-Machines-using-Windows-Server-Backup-in-Server-2008-R2.aspx
of:
http://www.virtualizationadmin.com/articles-tutorials/microsoft-hyper-v-articles/backup-recovery/installing-configuring-windows-server-backup-hyper-v.html
of bekijk onderstaande video:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windowsserver/dd775213.aspx
RECOVERY:
Om een individuele VM te restoren moet je de volgende commando’s uitvoeren:
In CMD:
Voer het commando: “wbadmin get versions” uit om te kijken welke backups aanwezig zijn.
Voer vervolgens het commando: “wbadmin get items -version:10/09/2010-10:08″ uit om de items in de backup te bekijken.
Onder het kopje “Application = Hyper-V” zie je GUIDs van de verschillende VMs.
Om te zien welke GUID bij welke VM hoort moet je onderstaand Powershell commando uitvoeren:
get-wmiobject -namespace “root\virtualization” -query “select * from msvm_computersystem” | format-table -property name, elementname
Als je onderstaand Powershell script in een ps1 opslaat en scheduled dan krijg je voortaan ook meldingen per email ofdat je backup gelukt is of niet.
===============================
$maxHours = 24
$email = “your@mail.net”
$smtpServer = “stmp.mail.net”
$sendSuccess = $true
## Script ————————————————————
Add-Pssnapin Windows.serverbackup
$summary = Get-WBSummary
$timeBetween = [DateTime]::Now – $summary.LastSuccessfulBackupTime
$computerName = get-content env:computername
if ($summary -eq $null)
{
$smtp = new-object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($email, $email, “BackupCheck.ps1 failed on $computerName”, “BackupCheck.ps1 failed with unknown error.”)
}
elseif ($timeBetween.TotalHours -gt $maxHours)
{
$smtp = new-object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($email, $email, “Windows Server Backup on $computerName failed”, “Last successfull backup on $computerName was at ” + $summary.LastSuccessfulBackupTime)
}
elseif ($sendSuccess)
{
$smtp = new-object Net.Mail.SmtpClient($smtpServer)
$smtp.Send($email, $email, “Windows Server Backup on $computerName was successfull”, “Last backup on $computerName was successfull at ” + $summary.LastSuccessfulBackupTime)
}
==============================
Mbv de Windows Recovery Environment zou het mogelijk moeten zijn om de gehele server inclusief de VM terug te zetten.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766048(WS.10).aspx
Abonneren op:
Posts (Atom)